Transport of Gases
Transport of Gases: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Oxyhaemoglobin,Transport of Oxygen,Transport of Gases etc.
Important Questions on Transport of Gases
Although much CO2 is carried in blood, bloods does not become acidic because
Which of these is correct regarding , and areas in the graph?
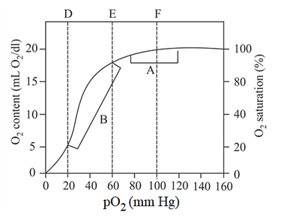
During one circuit of blood from the lungs to the tissues and back through the circulatory system, the percentage of haemoglobin giving up its oxygen to the tissues is
In our tissue level, the dissociation of oxyhaemoglobin occurs due to:
The oxyhaemoglobin dissociation curve may shift right if there is an increase of:
What is oxyhaemoglobin and how it is formed?
Explain the formation of oxyhaemoglobin.
How is oxyhaemoglobin formed?
When partial pressure of CO2 (PCO2) rises, the oxygen dissociation curve of haemoglobin will shift towards
The major fraction of released during cellular
respiration is transported by the blood to the lung capillaries
Or
Approximately seventy percent of carbon-dioxide absorbed by the blood will be transported to the lungs
From the following, which is the correct chemical formula of oxyhaemoglobin?
How does the transport of and happen in blood?
Bulk of carbon dioxide secreted from body tissues into the blood is present in the form of ______.
What is true about in humans?
Left side shift of oxygen-haemoglobin dissociation curve occurs during
Shape of dissociation curve is :-
Maximum volume of is transported as __A__ and of is transported as __B__. Select the option, which correctly fills and :-
The conditions which are favourable for the formation of oxyhaemoglobin are-
Oxygen is transported in blood mainly by
